Zero Trust: A Modern Blueprint for Secure Systems
When working with Zero Trust, a security model that assumes every user, device, and network flow could be compromised. Also known as Zero‑Trust Architecture, it shifts focus from traditional perimeter defenses to continuous verification of each request. In practice, Zero Trust requires that you never automatically trust anything inside or outside your network – you always verify, log, and enforce least‑privilege access. This mindset encompasses identity verification, micro‑segmentation, and real‑time analytics, creating a layered shield that narrows the attack surface and limits lateral movement for threat actors.
One of the core pillars supporting Zero Trust is Identity Verification, the process of confirming who a user or device claims to be before granting any access. Strong identity checks often combine passwords, biometrics, and multi‑factor authentication, turning each login into a high‑assurance event. Another essential component is Network Segmentation, the practice of dividing a network into isolated zones so that a breach in one area doesn’t spread unchecked. By slicing the infrastructure into micro‑segments, you enforce strict communication rules that only allow necessary traffic. Finally, regular Security Audits, independent evaluations of code, configurations, and processes feed the Zero Trust loop with fresh data, revealing gaps and confirming that controls remain effective over time. Together, these elements create a feedback cycle: audits inform better identity policies, which in turn tighten segmentation, continually reinforcing the Zero Trust stance.
Crypto exchanges and blockchain projects are fast adopters of Zero Trust because they handle high‑value assets and sensitive user data. Platforms like the ones reviewed on Market Pulse 11 – from DA.SG to Core Dao Swap – illustrate how zero‑trust principles shape fee models, audit frequencies, and user onboarding flows. When an exchange implements strict identity verification, enforces network segmentation for its trading engine, and subjects its smart contracts to rigorous security audits, it builds a stronger defense against hacks and compliance breaches. Readers will soon see detailed case studies, audit cost breakdowns, and practical tips that show Zero Trust in action across the crypto world. Dive into the collection below to discover how you can apply these practices to your own projects and stay ahead of emerging threats.
- Apr, 26 2025
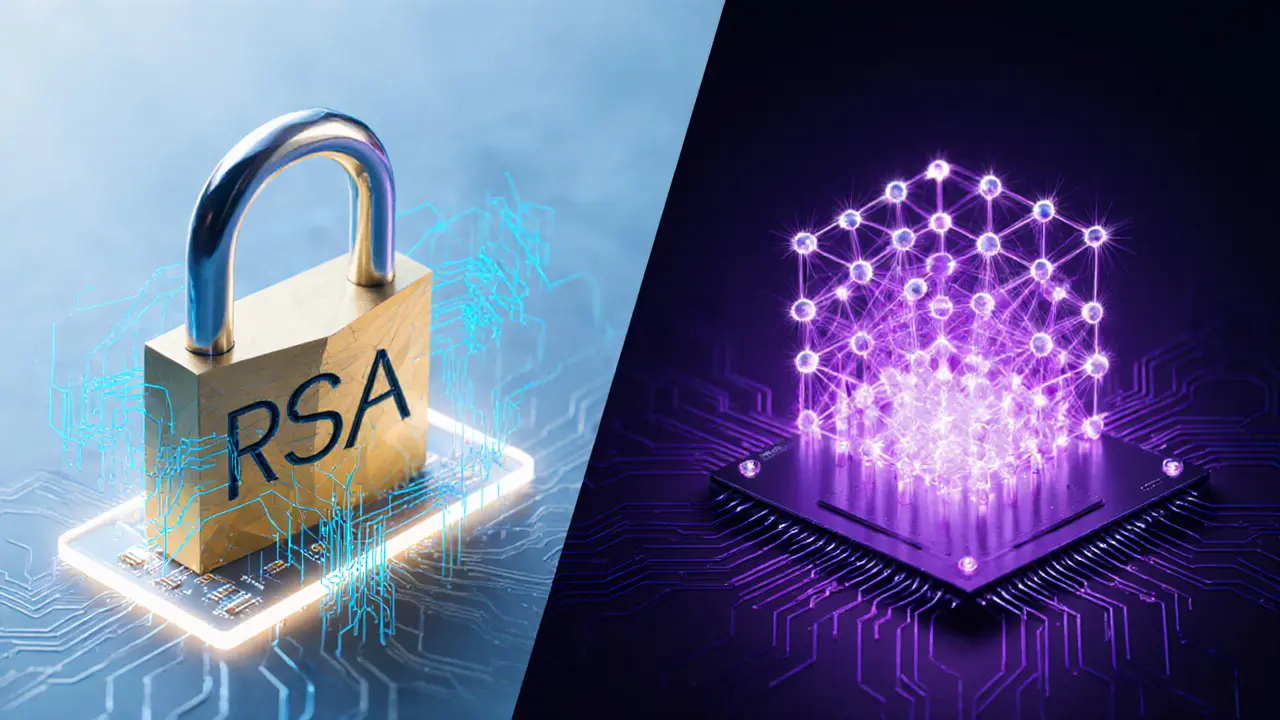
Explore why quantum computers threaten RSA, what post‑quantum cryptography is, and how organizations can build crypto‑agile, zero‑trust systems before the 2026 compliance deadline.
- Read More
